# Fiber 数据结构
# FiberRoot
上篇我们讲 render 的时候会创建 ReactRoot的时候会调用 createContainer 创建了 FiberRoot
在 react-reconciler/src/ReactFiberRoot.js 文件找到了 创建FiberRoot的方法
export function createFiberRoot(
containerInfo: any,
tag: RootTag,
hydrate: boolean,
hydrationCallbacks: null | SuspenseHydrationCallbacks,
): FiberRoot {
const root: FiberRoot = (new FiberRootNode(containerInfo, tag, hydrate): any);
if (enableSuspenseCallback) {
root.hydrationCallbacks = hydrationCallbacks;
}
const uninitializedFiber = createHostRootFiber(tag);
root.current = uninitializedFiber;
uninitializedFiber.stateNode = root;
initializeUpdateQueue(uninitializedFiber);
return root;
}
- 通过 FiberRootNode 创建 FiberRoot 实例
- 调用 createHostRootFiber 创建第一个 FiberNode
- 把 FiberNode 挂载到 FiberRoot 的current属性
- 把 FiberRoot 挂载到 FiberNode 的 stateNode 属性上
- 初始化 updateQueue
- 返回 FiberRoot
我们现在来看看 FiberRootNode 的结构
# FiberRootNode
function FiberRootNode(containerInfo, tag, hydrate) {
// root 类型 有legacy,batched,concurrent 分别对应 0|1|2
this.tag = tag;
// 当前应用对应的Fiber对象,是 RootFiber
this.current = null;
// root节点,render 方法接受的第二个参数
this.containerInfo = containerInfo;
// 只有在持久更新中用到,一般用不到
this.pendingChildren = null;
this.pingCache = null;
// 完成的过期时间
this.finishedExpirationTime = NoWork;
// 已经完成的任务的 FiberRoot对象,如果只有一个Root,拿它永远只可能是这个Root对应的Fiber,或者是null
// 在commit 阶段只会处理这个值对应的人物
this.finishedWork = null;
// 在任务被挂起的时候通过setTimeout设置的返回内容,用来下一次如果有新的任务挂起时清理还没触发的timeout
this.timeoutHandle = noTimeout;
// 顶层context对象,只有主动调用`renderSubtreeIntoContainer`时才会有用
this.context = null;
this.pendingContext = null;
// 用来确定第一次渲染的时候是否需要融合
this.hydrate = hydrate;
// 调用 Scheduler.scheduleCallback返回的节点
this.callbackNode = null;
// 与 root 相关联的回调优先级
this.callbackPriority = NoPriority;
// 树中存着的最早的过期时间
this.firstPendingTime = NoWork;
// 树中存着的最早的暂停过期时间
this.firstSuspendedTime = NoWork;
// 树中存着的最新暂停过期时间
this.lastSuspendedTime = NoWork;
// 暂停范围后的下一个已知到期时间
this.nextKnownPendingLevel = NoWork;
// 再次渲染的最新时间
this.lastPingedTime = NoWork;
// 再次渲染的过期时间
this.lastExpiredTime = NoWork;
if (enableSchedulerTracing) {
this.interactionThreadID = unstable_getThreadID();
this.memoizedInteractions = new Set();
this.pendingInteractionMap = new Map();
}
if (enableSuspenseCallback) {
this.hydrationCallbacks = null;
}
}
以上属性,我们现在也不知道有啥作用和含义,先暂时注释一下,在后面的分析中肯定会用到的
上面 FiberRoot 创建好了,我们来看看 rootFiber 也就是第一个 Fiber 对象的实例
# RootFiber
在上来创建 rootFiber 调用了createHostRootFiber
export function createHostRootFiber(tag: RootTag): Fiber {
let mode;
if (tag === ConcurrentRoot) {
mode = ConcurrentMode | BlockingMode | StrictMode;
} else if (tag === BlockingRoot) {
mode = BlockingMode | StrictMode;
} else {
mode = NoMode;
}
if (enableProfilerTimer && isDevToolsPresent) {
mode |= ProfileMode;
}
return createFiber(HostRoot, null, null, mode);
}
此方法先根据传递的tag进行mode的处理,然后返回函数 createFiber 的结果。代码很简单,就是返回一个 FiberNode 对象的实例,
const createFiber = function(
tag: WorkTag,
pendingProps: mixed,
key: null | string,
mode: TypeOfMode,
): Fiber {
return new FiberNode(tag, pendingProps, key, mode);
};
# FiberNode
Fiber对应一个组件需要被处理或者已经处理了,一个组件可以有一个或者多个Fiber
function FiberNode(
tag: WorkTag,
pendingProps: mixed,
key: null | string,
mode: TypeOfMode,
) {
// Instance
// WorkTag 一共22种 定义在 shared/ReactWorkTags 文件中
this.tag = tag;
// ReactElement里的key
this.key = key;
// ReactElement.type,也就是我们调用`createElement`的第一个参数 标签类型
this.elementType = null;
// 异步组件resolved之后返回的内容,一般是`function`或者`class`
this.type = null;
// 跟当前Fiber相关本地状态(比如浏览器环境就是DOM节点)
this.stateNode = null;
// Fiber
// 指向他在Fiber节点树中的`parent`,用来在处理完这个节点之后向上返回
this.return = null;
// 单链表结构,指向自己的第一个子节点
this.child = null;
// 指向自己的兄弟节点, return 指向同一个夫节点
this.sibling = null;
this.index = 0;
// ref 对象
this.ref = null;
// 更新所产生的props
this.pendingProps = pendingProps;
// 上一次渲染后的 props
this.memoizedProps = null;
// 存放 Fiber 对应组件产生的 update 队列
this.updateQueue = null;
// 上一次渲染后的 state
this.memoizedState = null;
// Fiber的依赖
this.dependencies = null;
// TypeOfMode 定义在 react-reconciler/src/ReactTypeOfMode.js 文件中
this.mode = mode;
// Effects
// 记录 side Effect
this.effectTag = NoEffect;
// 下一个 side Effect
this.nextEffect = null;
// 子树中第一个 side Effect
this.firstEffect = null;
// 子树中最后一个 side Effect
this.lastEffect = null;
// 代表任务在未来的哪个时间点应该被完成
this.expirationTime = NoWork;
// 快速确定子树中是否有不在等待的变化
this.childExpirationTime = NoWork;
// 在Fiber树更新的过程中,每个Fiber都会有一个跟其对应的Fiber
// 我们称他为`current <==> workInProgress`
// 在渲染完成之后他们会交换位置
this.alternate = null;
if (enableProfilerTimer) {
this.actualDuration = Number.NaN;
this.actualStartTime = Number.NaN;
this.selfBaseDuration = Number.NaN;
this.treeBaseDuration = Number.NaN;
this.actualDuration = 0;
this.actualStartTime = -1;
this.selfBaseDuration = 0;
this.treeBaseDuration = 0;
}
if (enableUserTimingAPI) {
this._debugID = debugCounter++;
this._debugIsCurrentlyTiming = false;
}
}
# 总结
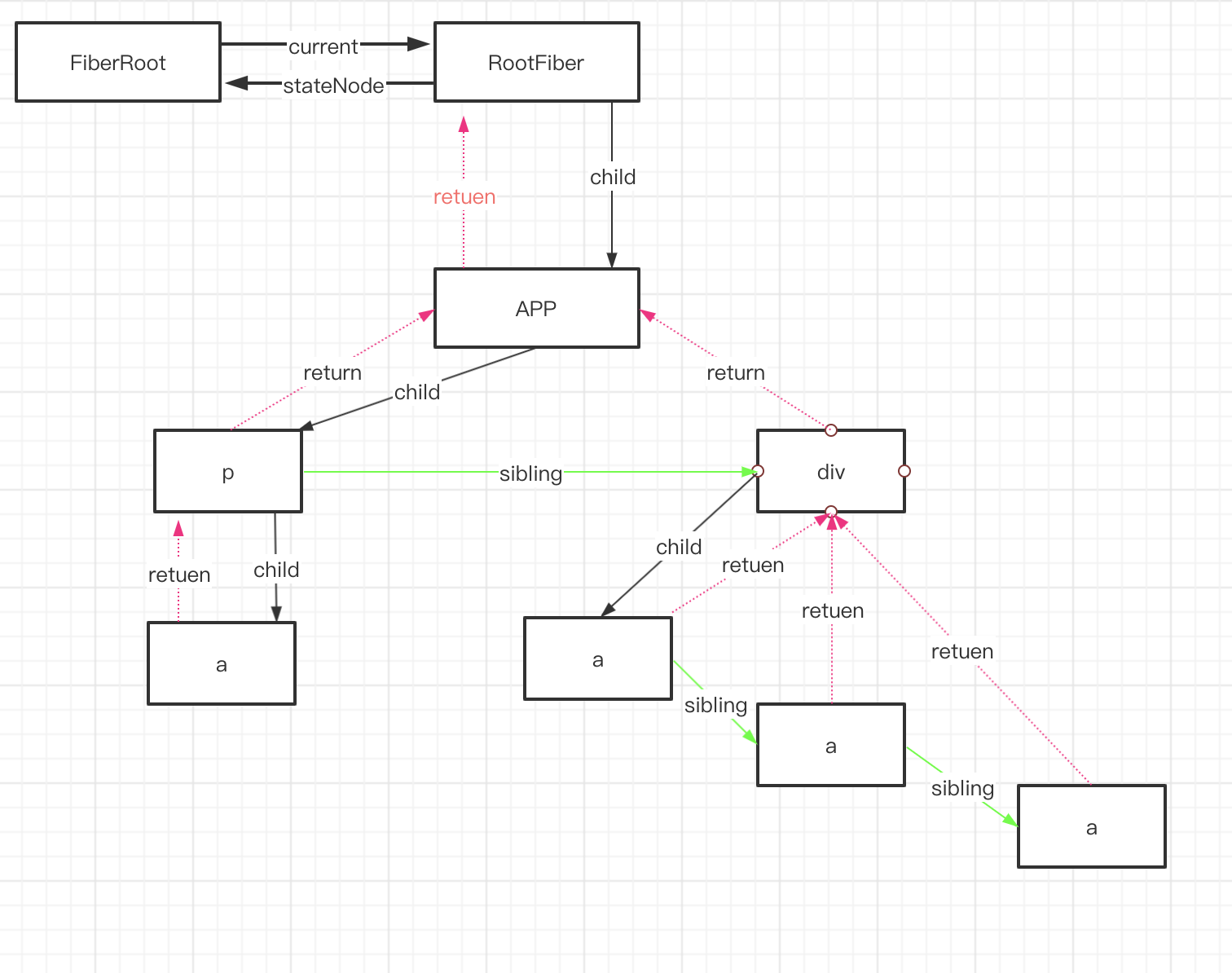
之前一直说 FiberRoot, RootFiber,Fiber,这些都是啊?之间有何关系? Fiber 到底是啥?
通过 Fiber 对象上的各个属性,我们可以知道
- 每个 ReactElement 对应一个 Fiber 对象
- Fiber 记录节点的各种状态
- Fiber 通过 return,child,sibling 串联整个应用形成的树结构
用一张图表示他们的结构